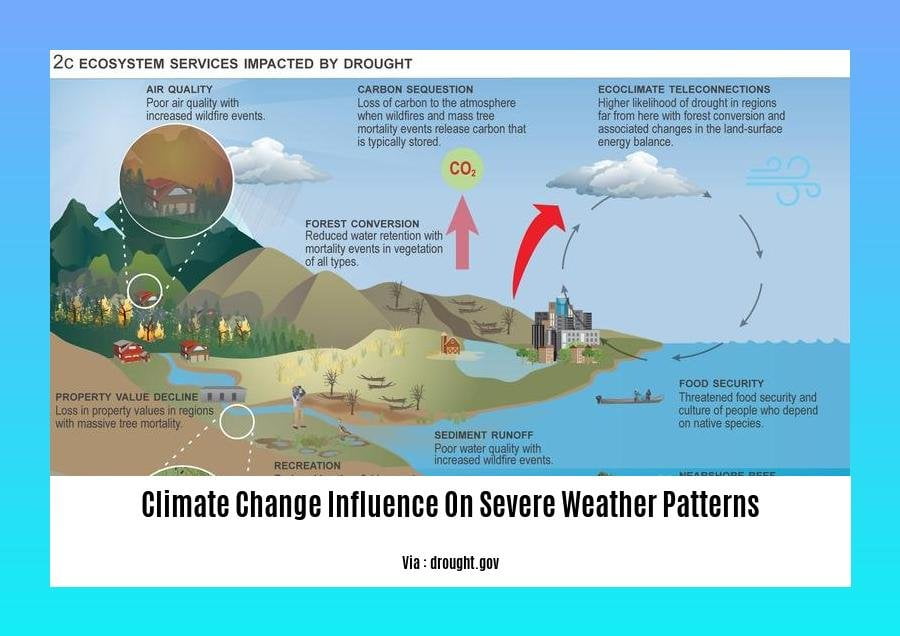
Unveiling the Complexities of Climate Change’s Influence on Severe Weather Patterns: As the planet grapples with the intensifying consequences of climate change, discerning its profound impact on extreme weather events becomes paramount. Witness the relentless escalation of scorching heat waves, the protracted destruction of wildfires, and the wrath of increasingly potent hurricanes. This article delves into the intricate interplay between human activities and the Earth’s climate system, deciphering the role of climate change in shaping these destructive weather patterns.
Key Takeaways:

- Climate change is changing temperature and precipitation patterns worldwide.
- These changes are influencing the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events.
- Heatwaves, droughts, wildfires, and floods are becoming more severe and last longer due to climate change.
- Human-caused climate change significantly increases the probability of extreme weather events.
Climate Change Influence on Severe Weather Patterns
As the planet warms, we are witnessing firsthand the escalating intensity and frequency of extreme weather events. This dramatic shift in global climate patterns is a direct result of human-induced climate change.
Understanding the Link: Climate Change Influence on Severe Weather Patterns
The Earth’s climate is a delicately balanced system, constantly adjusting to external influences. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and altering our climate norms.
Consequences of Climate Change Influence on Severe Weather Patterns
Heatwaves: Extended periods of extreme heat, exacerbated by climate change influence on severe weather patterns, pose serious health risks, contribute to drought, and can ignite devastating wildfires.
Droughts: Arid conditions intensified by climate change influence on severe weather patterns, lead to crop failures, water scarcity, and ecological imbalances.
Wildfires: Climate change is fueling an increase in both the frequency and severity of wildfires, fueled by drier vegetation and longer fire seasons.
Floods: Changing precipitation patterns and rising sea levels brought on by climate change influence on severe weather patterns contribute to increased flooding, damaging infrastructure and displacing communities.
Addressing the Challenge
Mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events requires a comprehensive approach:
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources and sustainable practices can drastically reduce the human contribution to climate change.
Adapt to Changing Conditions: Enhancing infrastructure resilience, improving weather forecasting, and implementing early warning systems can help communities withstand and recover from extreme weather.
Educate and Engage: Public awareness and education are crucial for fostering informed decision-making and galvanizing action to address climate change influence on severe weather patterns.
Learn more about the latest attribution of extreme weather events to global warming and how climate model projections for future disasters can influence severe weather patterns, including ways to mitigating climate-related disaster risks for the future.
Wildfires Burn Longer and Wider
Wildfires are becoming one of the most pressing challenges to society today. Wildfires burn longer and wider, a trend that is forecasted to continue as climate change intensifies.
In the past few years, we’ve seen some of the most destructive wildfires on record. These fires have caused widespread devastation, resulting in loss of life, property damage, and environmental degradation.
Factors Contributing to Longer and Wider Wildfires
Several factors contribute to the increasing severity and duration of wildfires, including:
- Climate Change: Climate change is leading to hotter and drier conditions, which provides ideal conditions for wildfires to thrive. Climate change also makes fire seasons longer, giving wildfires more time to spread and cause damage.
- Fuel Availability: The abundance of dry vegetation due to climate change, land-use practices, and other factors increases the availability of fuel for wildfires.
- Human Influence: Human activity, such as arson and accidental ignitions, is a major contributing factor to wildfires.
Consequences of Longer and Wider Wildfires
The impacts of longer and wider wildfires are far-reaching, including:
- Loss of Life and Property: Wildfires can cause widespread loss of life and property, as well as displacement of communities.
- Environmental Damage: Wildfires can cause significant damage to forests, grasslands, and other ecosystems, leading to soil erosion, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity.
- Economic Losses: Wildfires can have a devastating impact on local economies, costing governments and businesses billions of dollars in firefighting costs and post-fire recovery efforts.
Key Takeaways:
- Wildfires are becoming more severe and enduring due to climate change and other factors.
- Climate change-induced factors, such as hotter, drier conditions and longer fire seasons, are contributing to the increased severity and duration of wildfires.
- Wildfires have severe consequences, including loss of life, property damage, environmental damage, and economic losses.
Most Relevant URL Source:
Hurricanes Are Becoming More Intense
In the tapestry of climate change’s profound implications, the intensification of hurricanes emerges as a stark reality. Rising sea levels and a warming atmosphere conspire to fuel these storms with unprecedented destructive power.
Key Takeaways:
- Intensified Wind Speeds: Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for hurricanes, leading to higher wind speeds.
- Heavier Rainfall: A warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, resulting in torrential rainfall that exacerbates flooding.
- Slower Movement: Climate change alters atmospheric circulation patterns, causing hurricanes to linger longer over land, unleashing prolonged devastation.
- Increased Storm Surge: As sea levels rise, storm surge can penetrate further inland, threatening coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Sequential Hurricanes: Climate change may increase the frequency of back-to-back hurricanes, compounding the damage and recovery challenges.
Understanding these impacts is crucial for mitigating risks and building resilience. By unraveling the intricate web of climate change’s influence on hurricanes, we can better prepare for the intensifying storms that loom on the horizon.
Most Relevant URL Source:
– NASA’s Global Climate Change – Vital Signs of the Planet:

FAQ
Q1: How does human influence contribute to extreme weather events?
A1: Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to climate change. This change alters temperature and precipitation patterns, resulting in more intense and frequent extreme weather events.
Q2: Why are heatwaves becoming hotter and more persistent?
A2: Climate change is causing global temperatures to rise, intensifying heatwaves. These prolonged periods of extreme heat can have severe impacts on human health, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
Q3: How is climate change affecting wildfires?
A3: Climate change creates hotter and drier conditions, increasing the risk of wildfires. It also contributes to the drying out of vegetation, making landscapes more flammable. As a result, wildfires are becoming more severe and spreading beyond control.
Q4: What are the impacts of climate change on hurricane intensity?
A4: Climate change contributes to the intensification of hurricanes, leading to higher wind speeds and heavier rainfall. Rising sea levels also increase the severity of flooding during hurricanes.
Q5: How is climate change influencing sequential hurricanes?
A5: Climate change may increase the frequency of back-to-back hurricanes, also known as sequential hurricanes. These compounded events can cause extensive damage and disrupt communities for prolonged periods.